Analysis of key technical parameters of lead-acid batteries
2022-03-09 16:3101 Rated voltage
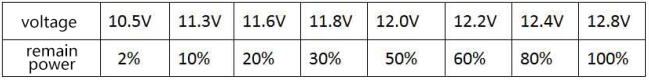
The actual voltage of the battery will be high when there is no load, and will decrease when there is a load. When there is a sudden large current discharge, the voltage will also suddenly decrease. There is an approximately linear relationship between battery voltage and remaining capacity, and this simple relationship exists only under no-load conditions.
The following are the reference values of the battery voltage and remaining capacity of the battery:
02 Maximum charge and discharge current
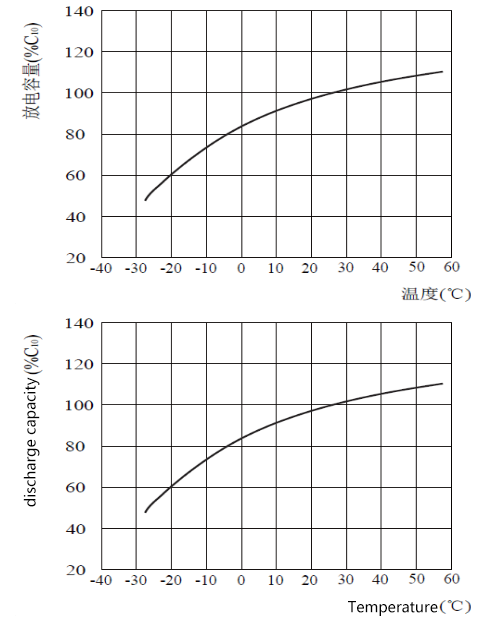
For example, if the battery capacity is C=100Ah and the charging current is 0.15C, it is 0.15×100=15A. The maximum charging current of the gel lead-acid battery is about 0.15C. Excessive charging current will affect the service life of the battery. Lead-carbon batteries are added with activated carbon to the negative electrode, which greatly increases the charging performance. For example, the parameter of 0.25C10 means that within 10 hours, the maximum charging current is 0.25*250=62.5A. In the table, the maximum discharge current of lead-carbon battery is 30I10, 10I10=C10, which means that within 10 hours, the maximum discharge current is 30*25=750A. The discharge current of gel lead-acid batteries is generally about 3I10.
The charging and discharging current of the battery has a lot to do with the system. If it is not designed well, it will affect the performance of the system. The charging current is related to the power of the components. For example, in a system, the components are 5kW and the voltage of the battery pack is 48V, then the maximum charging current of the battery is about 100A. If it is an ordinary lead-acid battery with a maximum current of 0.1C, the battery capacity should be at least 1000Ah; If it is a lead-carbon battery with a maximum current of 0.25C,the battery capacity should be at least 400Ah.
The discharge current is related to the load power. For example, in a system with a load of 10kW and a battery pack voltage of 48V, the maximum discharge current of the battery pack should reach 200A. For 30I10 lead-carbon battery it should reach more than 80Ah, and 800AH for gel battery.
03 Depth of discharge and cycle life
The depth of discharge is closely related to the life of the battery. The deeper the depth of discharge, the shorter the charging life.
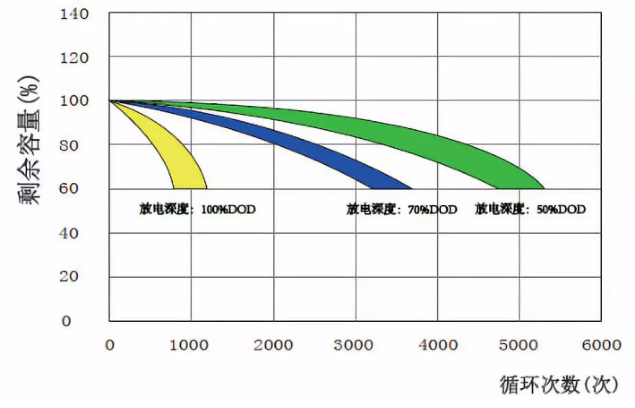
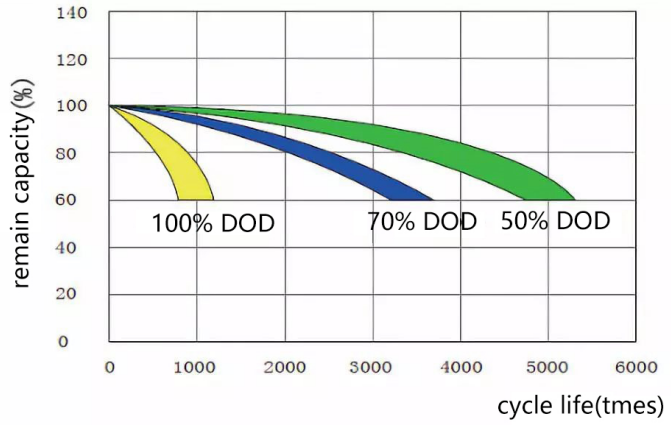
The cycle times of various batteries are different. The traditional stationary lead-acid battery is about 500 to 600 times; the starter lead-acid battery is about 300 to 500 times; the valve-regulated sealed lead-acid (VRLA) battery has a cycle life of 1000 to 1200 times.
The battery discharge depth is about 10% to 30% for shallow cycle discharge; the discharge depth is about 40% to 70% for medium cycle discharge; the discharge depth is about 80% to 90% for deep cycle discharge. The deeper the daily discharge depth of the long-term operation of the battery, the shorter the battery life; the shallower the discharge depth, the longer the battery life.
The picture shows the lead-carbon battery. When the depth of discharge is 50%, the cycle life is 4880 times, and the life is more than 12 years. When the depth of discharge is 70%, the cycle life is 3760 times, and the life is more than 10 years; the depth of discharge is 100%. When the cycle life is 998 times, the lifespan is less than 3 years. According to actual operating experience, a more moderate depth of discharge is 60% to 70%.
04 Power of lead acid battery
The power of the battery is divided into theoretical power and actual power. For example, for a 12V250Ah battery, the theoretical power is 12*250=3000Wh, which is 3 kWh, means the amount of electricity the battery can store; If the depth of discharge is 70%, the actual energy is 3000*70%=2100 Wh, which is 2.1 kWh, means the amount of electricity that can be used.