
6 main parameters of energy storage battery
2023-02-02 18:00Batteries are the most important part of the electrochemical energy storage systems, accounting for 60% of the cost of energy storage systems, PCS accounts for 20%, EMS accounts for 10%, BMS accounts for 5%, other accessories accounts for 5%. According to relevant data, China's energy storage battery shipments maintain a rapid growth trend, with an average annual growth rate of more than 50% in the next three years.
From the battery classification and characteristics, main performance parameters, energy storage application analysis, other concepts and other content, this article will help you have a better understanding of energy storage batteries and other content.
1. Classification and characteristics of batteries
The types of energy storage | Pumped energy storage |
Electrochemical energy storage | Lithium-ion battery |
Compressed air energy storage | Lead-acid battery | ||
Melting salt energy storage | sodium-sulfur cell | ||
Electrochemical energy storage | Flow redox battery | ||
Flywheel energy storage | Nickel battery | ||
Others |
According to the table, we can see that lead batteries and lithium batteries are widely used at this stage, lithium ion batteries are divided into three categories: consumer, power and energy storage.
Under the background that consumer batteries become saturated and power batteries are in the ascendant, changing product direction and entering the field of power and energy storage have become the strategic choice of many traditional consumer battery manufacturers.
1.1 Lead acid (carbon) battery
Lead-acid batteries can be used for power system backup power supply, solar and wind power generation and energy storage system, military and navigation equipment backup power supply, UPS backup power supply, emergency lighting, etc.
Lead carbon battery is a kind of capacitive lead-acid battery, its technology evolved from the traditional lead-acid battery. It is added with active carbon in the negative plates of lead-acid battery, which can significantly improve the life of lead-acid battery.
Valve-control sealed lead-acid storage battery GFM-200 | |
Vated voltage | 2V |
Rated capacity | 200AH |
Size(length*width*height) | 181*90*346 |
Internal resistance(full charge) | 0.69Ω |
Maximum discharge current | 1240A(5s) |
Self discharge(25℃) | <3% (30 days) |
Charging voltage | Floating charge:2.25V,single Equalized charge:2.35V,single |
griddle | M8 |
Recommended charging current | 30A |
Recommended use temperature | 15-25℃ |
【Explaination】
At present, due to its low initial cost, lead-acid batteries are widely used in projects with low charge and discharge frequency requirements. For example, the backup power supply of the communication base station, etc.
At the same time, due to the disadvantages of lead battery like low capacity density, short endurance time, high self-discharge rate, low cycle life, as a result, the proportion of lead battery in the energy field of energy storage application and electric vehicle field has gradually decreased.
1.2 Lithium battery
Lithium-ion battery is a secondary battery (rechargeable battery), which mainly depends on lithium ions moving between the positive electrode and the negative electrode to work.
Lithium battery adopts lithium metal or lithium alloy as the anode material and uses non-aqueous electrolyte solution, with advantages like high energy, long service life, light weight, widely used in hydraulic power, firepower, wind power, solar power station and other energy storage power system.
· Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery
· Ternary lithium battery (NCM / NCA) battery
· Lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) battery
· Other lithium batteries, such as lithium manganate battery, lithium titanate battery, etc
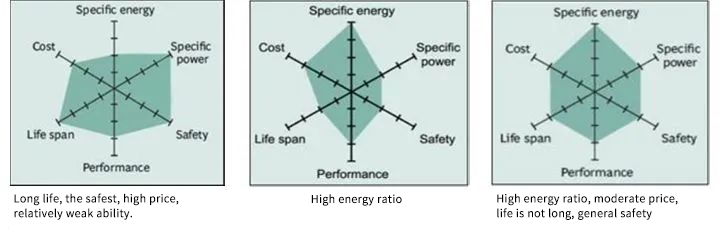
【Explaination】
In addition, in addition to the performance differences of different cell materials, the cell process types will also be significantly different:
1)Small cylinder type: service life of 5 years cost: low
2)Square: service life of 3 years cost: moderate
3)Metal cell: service life of 20 years cost: high
1.3 Sodium ion battery
Sodium ion battery is mainly composed of four parts: positive plates, negative plates, electrolyte and diaphragm,The structure and performance of the anode materials and cathode materials determine the sodium storage properties of the whole battery.
Compared with lithium ion batteries, sodium ions have large radius and volume, and their structural stability and dynamic performance are not advantageous, so more technological breakthroughs are needed. The focus of technology selection focuses on anode materials and cathode materials, which determines the performance and cost of sodium ion batteries
1.4 Flow redox battery
Flow redox battery is a battery technology in which the active material exists in the liquid electrolyte, the electrolyte is outside the reactor, under the push of the circulating pump, it flows through the reactor to realize the conversion of chemical energy and electric energy. International flow battery mainly has 4 technical routes, i.e. vanadium flow battery, zinc bromine battery, iron chromium battery, sodium polysulfide bromide battery.
2. Main battery performance parameters
Classification | essential parameter | US2000 |
Nominal parameters | nominal voltage (V) | 48 |
nominal capacity (AH) | 50 | |
configuration parameter | Size (mm) | 440*410*88.5 |
Weight (kg) | 24 | |
Electrical parameters | discharge voltage (V) | 45-54 |
charging voltage (V) | 52.5-54 | |
Maximum discharge current (A) | 100(2C)@15s | |
Rated discharge current (A) | 25 | |
Maximum charging current (A) | 100(2C)@15s | |
Rated charging current (A) | 25 | |
Other parameters | working temperature (℃) | 0-50 |
communication interface | RS232,RS485,CAN | |
cycle index (Times) | >6000(80%DOD) |
48V energy storage lithium battery parameters
2.1 Ah (Ampere hours)
Reflect the battery capacity.
[Explaination]
Nominal voltage and nominal amper hour are the most basic and core concepts of the battery. Electric quantity Wh= power W * hour h = voltage V * amper hours Ah
2.2 C (Battery discharge rate)
Reflect the battery charge and discharge capacity ratio;
charge and discharge ratio = charge and discharge current / rated capacity.
[Explaination]
A measure of the discharge speed. Generally, the capacity of the battery can be detected by different discharge currents.
2.3 DOD(Depth of Discharge)
Refers the percentage of the capacity released by the battery to the rated capacity of the battery during its use.
[Explaination]
For the same cell, the set DOD is inversely proportional to the cell cycle life. When one aspect of performance is improved, other aspects of performance are sacrificed.
Recycle life
DOD | Battery recycle times | life |
80% | >6000 times | ≈8years |
85% | > 5000times | ≈7years |
The relationship between the DOD and the cycle numbers of cell
2.4 SOC (State of charge)
It means the percentage of the battery power remaining in the rated battery capacity.
2.5 SOH(State of Health)
The health state of the battery (including capacity, power, internal resistance, etc.) is the ratio of the capacity released by the battery discharged from the full charge state at a certain rate to the cut-off voltage to the corresponding nominal capacity.
[Explaination]
Simply speaking, it is the ratio of performance parameters to nominal parameters after battery use for a period of time, new factory battery is 100%, completely scrapped is 0%, according to the IEEE standard, batteries should be replaced when they have been used for a period of time and their capacity on a full charge is less than 80% of their rated capacity.
2.6 Three stages
Three-stage charging generally refers to a three-stage charging device, three-stage charging is an automatic charging process. Constant current, constant pressure and floating charge are the three necessary stages of three-stage charging.
The charge-discharging strategy of lead-acid battery is three-stage::
1st stage is fast charge: Constant current charging stage
2nd stage is equlized charge constant voltage charging stage
3rd stage is floating charge mode:
3.Other concepts of the battery
3.1 Power battery and backup battery
Power battery is suitable for long-time discharge, applied in electric vehicle battery, photovoltaic energy storage battery, etc., but because of the few plates, few chemical contact surface, it can only discharge at the rate of 0.1~2C. The backup battery is used for the backup power supply after power failure. Due to the low use condition, the backup battery life can reach 8 to 10 years. UPS is typical example.
3.2 Lithium battery cascade utilization
With the rise of electric vehicles, the use of lithium batteries has greatly increased. After the retirement, lithium iron phosphate power batteries can be used as energy storage batteries for 3 to 5 years.
After reading this article, how many following vocabulary do you remember?
AH | C | DOD | SOC |
SOH | BMS | BMU | EMS |
DC/AC coupling | PCS | LEP | NCM/NCA |
UPS/EPS | Back battery | power battery | cascade utilization |
